 Greg Koukl tries to hold atheists’ feet to the fire to show how they misuse moral thinking. His analysis provides good instruction in poor argumentation, but not quite in the way he hopes.
Greg Koukl tries to hold atheists’ feet to the fire to show how they misuse moral thinking. His analysis provides good instruction in poor argumentation, but not quite in the way he hopes.
The podcast is “Making Sense of Morality” (3/6/11). As I quote Koukl below, I will use approximate time markers from the audio stream.
He starts by claiming that there are objective moral values. He didn’t define them, but William Lane Craig’s definition works: “moral values that are valid and binding whether anybody believes in them or not.”1 That’s a big claim—these are moral values that are somehow grounded supernaturally or transcendentally. Never having seen evidence for supernatural or transcendent anything, I was eager to hear Koukl justify their existence. Here he goes:
Virtually no one believes the opposite. (3:23)
And that’s it. Apparently, Koukl has no argument besides, “You believe that … right?” We’re not off to a good start.
From this flabby grounding, he proposes to dismantle what many Christian apologists have admitted is the most challenging problem they face, the Problem of Evil. There is no Problem of Evil, Koukl says, unless there are objective moral values.
Such a problem could only exist if morals were objective, not relative, because we can only complain about the existence of a good powerful god with regards to the existence of evil in the world if there is actually objectively, really evil in the world, not just “evil” in our own preferences. (4:20)
No. The Problem of Evil simply points out a paradox: the Christian imagines (1) a good god who (2) tolerates a world with plenty of evil in it. How is this possible?
This is quite simple: you, Greg, would not be called good if (for example) you had the power to diffuse the tectonic energy that caused the Haiti earthquake that killed 300,000 people but didn’t—this is the Word Hygiene argument. The words “good” and “evil” are defined in the dictionary, and we don’t change the definitions when we talk about God. No objective anything is required—the Problem of Evil simply assumes that your god exists for the sake of the argument, and then it takes this idea for a drive and runs it off the unavoidable logical cliff.
Koukl continues, noting that atheists often say that evolution can explain morality. But:
[Evolution] is not going to get you a genuine, bona fide objective moral obligation; it’s just going to get you maybe the feeling of morality when morality doesn’t actually exist. (6:03)
Koukl is saying that morality is either objective or it’s nothing.
So let’s check the dictionary. “Moral” is defined as “of or relating to principles of right and wrong in behavior; ethical” or “conforming to a standard of right behavior” (Merriam-Webster). And what are these principles and standards? I suggest that they’re the laws and customs of society. The dictionary mentions no objective, supernatural, or absolute anything. Evolution programs us with moral instincts; Koukl’s imagined concern vanishes.
Next, Koukl talked about listening to an interview with professor and author Steven Stuart Williams. Williams rejected objective morality and said that we should minimize suffering. But why does he say this?
Because that’s the way I like it. (10:15)
(Note that this is Koukl’s paraphrase of Williams’ answer.) This seemed to be a bombshell to Koukl, though I don’t see why. That could be a clumsy paraphrase of my own thinking: that we strive to minimize suffering because our programming (our conscience) tells us to. This conscience punishes us with guilt when we resist it—when we didn’t stop to help someone or when we took an action that caused harm.
Why is this shocking? Greg, isn’t this the way it works for you?
The interviewer next asked Williams how he would counter a Stalin or Pol Pot.
By what standard does [Williams] say that his preference is a better morally speaking preference than those other preferences that are opposite his? And for this he had no answer. (12:30)
That’s okay—I have an answer. This is just the moral relativism fallacy. Koukl apparently imagines a dilemma: you must accept either
- objective morality, with a supernatural or transcendental grounding for morality, or
- relative morality, where I have my moral truths and you have yours, and I have no ability to criticize.
The problem is that this doesn’t define all the options. I see no evidence for objective morality (and Koukl doesn’t provide any), but I’m quite happy to criticize moral claims with which I don’t agree.
I think we have a shared (not objective) grounding in the programming common to all humans. That is, we aren’t seeing God’s universal moral truth but rather universally held moral instincts. Wouldn’t that explain the facts?
And now it’s time to get in a dig at the New Atheists. Koukl says that the “old time atheists” were much more intellectually honest. They followed their thinking to its logical conclusion and took their medicine, whatever that was. He cautioned his Christian listeners about slippery atheists playing games.
The old style guys would bite the bullet and they’d say, “Nope, no morality, no right and wrong, all personal preferences, just emotions … no meaning in life.” (14:50)
If you want to debate the “old style guys,” Greg, go ahead, but this doesn’t describe me. I have plenty of morality and meaning in my life, but thanks for asking. It’s just not supernaturally grounded … but then there’s no reason to think yours is, either.
So what you’re saying is, there is no transcendent morality, it is just a matter of personal opinion, and when you are put up against Mao Tse-tung, you can’t give me a reason why one person would choose one rather than the other. (15:50)
Can Koukl have never had an argument about a moral issue? Each person makes a case using the shared moral ideas of our species and culture—that’s how it’s done. Or look at a legislative debate for a more formal example.
Bizarrely, the interviewer then asks,
Wouldn’t it be more satisfying to have God ground [morality] on a purely pragmatic basis? (16:25)
Do you hear what you’re saying? You’re wondering if reality is satisfying? As if we have a choice! It’s reality—we’re stuck with it! The focus should be on figuring out what reality is and working with it.
Williams argued that he could live a good life, but Koukl accuses him of playing word games:
What exactly do you mean by “good” here? I know what he meant by “good”; he meant by “good” the same thing his theistic interviewer meant by “good.” The problem is, he has no right to those terms because they aren’t at home in the worldview he was arguing for. (18:20)
And we’re back to consulting the dictionary. Show me the objective part of the definition of “good” that would make it inappropriate if said by an atheist. We have a common definition for words; that’s how communication works. Where’s the problem?
When we say we can punish people for doing bad, [Williams means] that we could still punish people for doing things that are contrary to [his] personal preference. (20:45)
Duh—doesn’t everyone want laws to be in accord with their own views of right and wrong? We make compromises as members of a society, but obviously we’d like the laws to be as in line with our personal morality as possible.
Koukl ends by encouraging his listeners to listen carefully to make sure the other guy is using moral language and concepts correctly.
Finally—something we can agree on.
Photo credit: Wikipedia
1William Lane Craig and Walter Sinnott-Armstrong, God? A Debate Between a Christian and an Atheist (Oxford University Press, 2004), p. 17.
Related links:
- “Morality 1: Good without Gods,” QualiaSoup (video, 13:25), 6/23/11.
- “Morality 2: Not-so-good Books,” QualiaSoup (video, 14:10), 7/28/11.
- “Morality 3: Of Objectivity and Oughtness,” QualiaSoup (video, 17:12), 11/6/11.
 Welcome to post #100! It’s time to see how far this blog has come since I started last August.
Welcome to post #100! It’s time to see how far this blog has come since I started last August.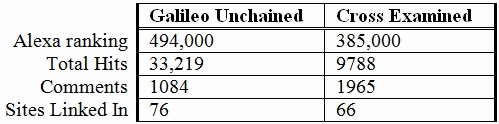



 It’s time once again to check in with apologist Greg Koukl. In a recent podcast (“
It’s time once again to check in with apologist Greg Koukl. In a recent podcast (“
 Greg Koukl tries to hold atheists’ feet to the fire to show how they misuse moral thinking. His analysis provides good instruction in poor argumentation, but not quite in the way he hopes.
Greg Koukl tries to hold atheists’ feet to the fire to show how they misuse moral thinking. His analysis provides good instruction in poor argumentation, but not quite in the way he hopes.